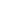
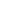
1. Visual Inspection
Observe the linkage surface for cracks, rust, deformation, or missing parts.
Check the integrity of key components such as joints, rollers, and brackets.
2. Functional Test
Turn on the wiper switch and observe whether the wiper arm moves smoothly. If there is any sticking, intermittent pauses, or noise, it may be caused by internal binding or wear of the linkage.
Gently pull on the wiper arm to feel for any unusual resistance or looseness.
3. Sound and Vibration
During normal operation, there should only be a slight mechanical sound. Any metallic clattering, unusual vibration, or noise often indicates damage to the gears or bearings inside the linkage.
4. Professional Inspection
Using a multimeter to measure the internal resistance of the linkage or inspecting the limit switches can further confirm whether the motor or linkage is faulty.
The above methods are widely used in industry maintenance. Image analysis of the images provided here shows no signs of breakage, deformation, or abnormal wear, indicating that the linkage is in normal condition.
What is the device that controls the wiper linkage called?
The device that controls the wiper linkage is often referred to as the "wiper control system" in automotive technical literature. Its core components include:
1. Wiper switch: The handle or button operated by the driver.
2. Wiper control unit: The electronic control unit that receives the switch signal and drives the wiper motor.
3. Wiper motor: The power source that actually generates the mechanical movement.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Deutsch
Deutsch